
国际口腔医学杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 755-763.doi: 10.7518/gjkq.2025091
Xinyu Wen( ),Mo Zhou,Ruolin Ding,Ruiyang Ren,Zhihe Zhao(
),Mo Zhou,Ruolin Ding,Ruiyang Ren,Zhihe Zhao( )
)
摘要:
正畸治疗作为矫治错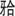 _畸形的有效方式,可有效提升患者咀嚼和美观功能;但矫治器的各部分装置妨碍了口腔卫生清洁,增大了患者罹患龋病、龈炎和牙周病的风险。冲牙器作为新型的口腔清洁工具,已成为正畸患者口腔清洁的辅助方式之一。本文综述了冲牙器的工作原理及应用情况、正畸患者的口腔卫生特点以及冲牙器在正畸患者口腔卫生清洁中的应用效果,总结发现:冲牙器利用脉冲水流冲击以清洁口腔,可以抑制菌斑的形成和附着,作为辅助清洁方式是有效的,推荐用于邻间刷和牙线不易达到的部位。
_畸形的有效方式,可有效提升患者咀嚼和美观功能;但矫治器的各部分装置妨碍了口腔卫生清洁,增大了患者罹患龋病、龈炎和牙周病的风险。冲牙器作为新型的口腔清洁工具,已成为正畸患者口腔清洁的辅助方式之一。本文综述了冲牙器的工作原理及应用情况、正畸患者的口腔卫生特点以及冲牙器在正畸患者口腔卫生清洁中的应用效果,总结发现:冲牙器利用脉冲水流冲击以清洁口腔,可以抑制菌斑的形成和附着,作为辅助清洁方式是有效的,推荐用于邻间刷和牙线不易达到的部位。
中图分类号:
| [1] | Zhao NR, Guo YN, Cui SJ, et al. Microbiological advances in orthodontics: an overview and detailed analysis of temporary anchorage devices[J]. Curr Med Sci, 2022, 42(6): 1157-1163. |
| [2] | Wang Y, Xu JC, Yu CH, et al. Prevention of bacte-rial biofilm formation on orthodontic brackets by non-crosslinked chitosan coating[J]. Int J Biol Ma-cromol, 2023, 251: 126283. |
| [3] | Braga AS, Simas LLM, Pires JG, et al. Antibiofilm and anti-caries effects of an experimental mouth rinse containing Matricaria chamomilla L. extract under microcosm biofilm on enamel[J]. J Dent, 2020, 99: 103415. |
| [4] | Richards D. Chlorhexidine mouthwash plaque le-vels and gingival health[J]. Evid Based Dent, 2017, 18(2): 37-38. |
| [5] | Claydon NC. Current concepts in toothbrushing and interdental cleaning[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2008, 48: 10-22. |
| [6] | Flemmig TF, Epp B, Funkenhauser Z, et al. Adjunctive supragingival irrigation with acetylsalicylic a-cid in periodontal supportive therapy[J]. J Clin Perio-dontol, 1995, 22(6): 427-433. |
| [7] | Mohapatra S, Rajpurohit L, Mohandas R, et al. Comparing the effectiveness of water flosser and dental floss in plaque reduction among adults: a systematic review[J]. J Indian Soc Periodontol, 2023, 27(6): 559-567. |
| [8] | Matthes R, Jablonowski L, Pitchika V, et al. Efficiency of biofilm removal by combination of water jet and cold plasma: an in-vitro study[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2022, 22(1): 157. |
| [9] | Kato K, Tamura K, Nakagaki H. Quantitative evalua-tion of the oral biofilm-removing capacity of a dental water jet using an electron-probe microanalyzer[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2012, 57(1): 30-35. |
| [10] | Xu X, Zhou YS, Liu CC, et al. Effects of water flossing on gingival inflammation and supragingival plaque microbiota: a 12-week randomized controlled trial[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2023, 27(8): 4567-4577. |
| [11] | Cutler CW, Stanford TW, Abraham C, et al. Clinical benefits of oral irrigation for periodontitis are rela-ted to reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and plaque[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2000, 27(2): 134-143. |
| [12] | Bertl K, Geissberger C, Zinndorf D, et al. Bacterial colonisation during regular daily use of a power-driven water flosser and risk for cross-contamination. Can it be prevented[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2022, 26(2): 1903-1913. |
| [13] | Bertl K, Edlund Johansson P, Bruckmann C, et al. Bacterial colonization of a power-driven water flos-ser during regular use. A proof-of-principle study[J]. Clin Exp Dent Res, 2021, 7(5): 656-663. |
| [14] | Worthington HV, MacDonald L, Poklepovic Pericic T, et al. Home use of interdental cleaning devices, in addition to toothbrushing, for preventing and controlling periodontal diseases and dental caries[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 4(4): CD012018. |
| [15] | Sarkisova F, Morse Z, Lee K, et al. Oral irrigation devices: a scoping review[J]. Clin Exp Dent Res, 2024, 10(3): e912. |
| [16] | Schüz B, Wiedemann AU, Mallach N, et al. Effects of a short behavioural intervention for dental flos-sing: randomized-controlled trial on planning when, where and how[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2009, 36(6): 498-505. |
| [17] | Al Khamis S, Asimakopoulou K, Newton T, et al. The effect of dental health education on pregnant women’s adherence with toothbrushing and flos-sing-a randomized control trial[J]. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol, 2017, 45(5): 469-477. |
| [18] | Altalhi AM, Alqahtani NS, Alareefi JA, et al. A comparative review of water flossers in periodontal the-rapy[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(12): e50162. |
| [19] | Ge Y, Bamashmous S, Mancinelli-Lyle D, et al. Interdental oral hygiene interventions elicit varying compositional microbiome changes in naturally occurring gingivitis: secondary data analysis from a clinical trial[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 2024, 51(3): 309-318. |
| [20] | Abdellatif H, Alnaeimi N, Alruwais H, et al. Comparison between water flosser and regular floss in the efficacy of plaque removal in patients after single use[J]. Saudi Dent J, 2021, 33(5): 256-259. |
| [21] | Lang NP, Räber K. Use of oral irrigators as vehicle for the application of antimicrobial agents in chemical plaque control[J]. J Clin Periodontol, 1981, 8(3): 177-188. |
| [22] | Kim JM, Yoo SY, An JS, et al. Effect of a multichannel oral irrigator on periodontal health and the oral microbiome[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 12043. |
| [23] | Gänzer H, Kasslatter M, Wiesmüller V, et al. Clean-sing efficacy of an oral irrigator with microburst technology in adolescent orthodontic patients. A randomized-controlled crossover study[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2024, 28(10): 524. |
| [24] | Mancinelli-Lyle D, Qaqish JG, Goyal CR, et al. Efficacy of water flossing on clinical parameters of inflammation and plaque: a 4-week randomized controlled trial[J]. Int J Dent Hyg, 2023, 21(4): 659-668. |
| [25] | Salles MM, Oliveira VC, Macedo AP, et al. Bru-shing associated with oral irrigation in maintaining implants and overdentures hygiene-a randomized clinical trial[J]. Odontology, 2021, 109(1): 284-294. |
| [26] | Ren XL, He J, Cheng R, et al. The efficacy and safety of oral irrigator on the control of dental plaque and gingivitis: a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group clinical trial[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2023, 20(4): 3726. |
| [27] | Lainson PA, Bergquist JJ, Fraleigh CM. A longitudinal study of pulsating water pressure cleansing devices[J]. J Periodontol, 1972, 43(7): 444-446. |
| [28] | Hoover DR, Robinson HBG. The comparative effectiveness of a pulsating oral irrigator as an adjunct in maintaining oral health[J]. J Periodontol, 1971, 42(1): 37-39. |
| [29] | Sharma NC, Lyle DM, Qaqish JG, et al. Effect of a dental water jet with orthodontic tip on plaque and bleeding in adolescent patients with fixed orthodontic appliances[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2008, 133(4): 565-571, 628.e1-e2. |
| [30] | Koopman JE, van der Kaaij NC, Buijs MJ, et al. The effect of fixed orthodontic appliances and fluoride mouthwash on the oral microbiome of adolescents-a randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9): e0137318. |
| [31] | Guo RZ, Liu H, Li XB, et al. Subgingival microbial changes during the first 3 months of fixed appliance treatment in female adult patients[J]. Curr Micro-biol, 2019, 76(2): 213-221. |
| [32] | Guo RZ, Zheng YF, Liu H, et al. Profiling of subgingival plaque biofilm microbiota in female adult patients with clear aligners: a three-month prospective study[J]. PeerJ, 2018, 6: e4207. |
| [33] | Liu Y, Shi X, Lin GB, et al. Effects of periodontal initial therapy combined with orthodontic treatment on anterior tooth function and inflammatory factors in gingival crevicular fluid in patients with perio-dontal disease induced anterior tooth displacement[J]. Pak J Med Sci, 2023, 39(6): 1620-1625. |
| [34] | Jepsen K, Sculean A, Jepsen S. Complications and treatment errors involving periodontal tissues rela-ted to orthodontic therapy[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2023, 92(1): 135-158. |
| [35] | Hashem G, Zhang Q, Hayami T, et al. Relaxin and beta-estradiol modulate targeted matrix degradation in specific synovial joint fibrocartilages: progeste-rone prevents matrix loss[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2006, 8(4): R98. |
| [36] | Papageorgiou SN, Xavier GM, Cobourne MT, et al. Effect of orthodontic treatment on the subgingival microbiota: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Orthod Craniofac Res, 2018, 21(4): 175-185. |
| [37] | Ghijselings E, Coucke W, Verdonck A, et al. Long-term changes in microbiology and clinical periodontal variables after completion of fixed orthodontic appliances[J]. Orthod Craniofac Res, 2014, 17(1): 49-59. |
| [38] | Cosma LL, Şuhani RD, Mesaroş A, et al. Current treatment modalities of orthodontically induced white spot lesions and their outcome-a literature review[J]. Med Pharm Rep, 2019, 92(1): 25-30. |
| [39] | Salerno C, Grazia Cagetti M, Cirio S, et al. Distribution of initial caries lesions in relation to fixed ortho-dontic therapy. A systematic review and meta-ana-lysis[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2024, 46(2): cjae008. |
| [40] | Chapman JA, Roberts WE, Eckert GJ, et al. Risk factors for incidence and severity of white spot lesions during treatment with fixed orthodontic app-liances[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2010, 138(2): 188-194. |
| [41] | Tan A, Çokakoğlu S. Effects of adhesive flash-free brackets on enamel demineralization and periodontal status[J]. Angle Orthod, 2020, 90(3): 339-346. |
| [42] | 徐瑛, 吕锦. 冲牙器改善成人固定正畸患者牙周健康效果评价[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2016, 32(4): 405-407. |
| Xu Y, Lü J. Evaluation of oral irrigator on impro-ving periodontal health for adult orthodontic treatment with fixed appliance[J]. J Oral Sci Res, 2016, 32(4): 405-407. | |
| [43] | Tyler D, Kang J, Goh HH. Effectiveness of Waterpik® for oral hygiene maintenance in orthodontic fixed appliance patients: a randomised controlled trial[J]. J Orthod, 2023, 50(4): 367-377. |
| [44] | Al Hariri MH, Karkoutly M, Al Kurdi S, et al. The efficacy of the dental Water Jet, orthodontic, and conventional toothbrushes in plaque removal around orthodontic braces in adolescents: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Clin Exp Dent Res, 2023, 9(4): 606-613. |
| [45] | Erbe C, Klukowska M, Timm HC, et al. A rando-mized controlled trial of a power brush/irrigator/mouthrinse routine on plaque and gingivitis reduction in orthodontic patients[J]. Angle Orthod, 2019, 89(3): 378-384. |
| [46] | Sawan N, Ben Gassem A, Alkhayyal F, et al. Effectiveness of super floss and water flosser in plaque removal for patients undergoing orthodontic treatment: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Int J Dent, 2022, 2022: 1344258. |
| [47] | AlMoharib HS, Alqasem A, Almusfer G, et al. The effectiveness of water jet flossing and interdental flossing for oral hygiene in orthodontic patients with fixed appliances: a randomized clinical trial[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2024, 24(1): 498. |
| [48] | Wiesmüller V, Kasslatter M, Zengin B, et al. Clean-sing efficacy of an oral irrigator with microburst technology in orthodontic patients-a randomized-controlled crossover study[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2023, 27(5): 2089-2095. |
| [49] | Caccianiga P, Nota A, Tecco S, et al. Efficacy of home oral-hygiene protocols during orthodontic treatment with multibrackets and clear aligners: microbiological analysis with phase-contrast microscope[J]. Healthcare, 2022, 10(11): 2255. |
| [50] | Christou V, Timmerman MF, van der Velden U, et al. Comparison of different approaches of interdental oral hygiene: interdental brushes versus dental floss[J]. J Periodontol, 1998, 69(7): 759-764. |
| [51] | AlMoharib HS, AlAskar MH, AlShabib AN, et al. The effectiveness of dental water jet in reducing dental plaque and gingival bleeding in orthodontic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials[J]. Int J Dent Hyg, 2024, 22(1): 56-64. |
| [52] | Jiang Q, Li JL, Mei L, et al. Periodontal health du-ring orthodontic treatment with clear aligners and fixed appliances: a meta-analysis[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 2018, 149(8): 712-720.e12. |
| [53] | Maslamani GE, Muharraq EH, Abujamilah EE, et al. Effectiveness of water flossers in orthodontic treatment: a systematic review[J]. Saudi J Oral Dent Res, 2023, 8(12): 396-403. |
| [54] | 孙文韬, 王依玮, 钱洁蕾, 等. 便携式冲牙器对牙龈炎症患者口腔卫生维护效果的研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 40(11): 1505-1508. |
| Sun WT, Wang YW, Qian JL, et al. Study on portable dental irrigator for oral hygiene in patients with gingival inflammation[J]. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Med Sci), 2020, 40(11): 1505-1508. | |
| [55] | 李婵秀, 黄南楠, 王萍. 冲牙器对老年牙周病患者牙菌斑和牙龈炎症的抑制作用[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2013, 27(11): 1139-1140. |
| Li CX, Huang NN, Wang P. Inhibitory effect of oral irrigator on dental plaque and gingival inflammation in elderly patients with periodontal disease[J]. J Chin Pract Diag Ther, 2013, 27(11): 1139-1140. | |
| [56] | Salles MM, de Cássia Oliveira V, Macedo AP, et al. Effectiveness of brushing associated with oral irrigation in maintenance of peri-implant tissues and overdentures: clinical parameters and patient satisfaction[J]. J Oral Implantol, 2021, 47(2): 117-123. |
| [57] | Ioannidis A, Thurnheer T, Hofer D, et al. Mechanical and hydrodynamic homecare devices to clean rough implant surfaces-an in vitro polyspecies biofilm study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2015, 26(5): 523-528. |
| [58] | Sirinirund B, Siqueira R, Li JY, et al. Effects of crown contour on artificial biofilm removal efficacy with interdental cleaning aids: an in vitro study[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2023, 34(8): 783-792. |
| [59] | Tütüncüoğlu S, Cetinkaya BO, Pamuk F, et al. Clinical and biochemical evaluation of oral irrigation in patients with peri-implant mucositis: a randomized clinical trial[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2022, 26(1): 659-671. |
| [60] | Louropoulou A, Slot DE, Van der Weijden F. Mechanical self-performed oral hygiene of implant supported restorations: a systematic review[J]. J Evid Based Dent Pract, 2014, 14 (): 60-69.e1. |
| [61] | AlMoharib HS, AlAskar MH, Abuthera EA, et al. Efficacy of three interdental cleaning methods for peri-implant health maintenance of single implant-supported crowns: a randomised clinical trial[J]. Oral Health Prev Dent, 2024, 22: 51-56. |
| [62] | Bunk D, Eisenburger M, Häckl S, et al. The effect of adjuvant oral irrigation on self-administered oral care in the management of peri-implant mucositis: a randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2020, 31(10): 946-958. |
| [1] | 张俭,白雪,何小倩,葛振林. 多模态数据融合技术在口腔正畸领域的应用及研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(6): 764-770. |
| [2] | 胡凯,张延晓,毛丙永,唐鑫,王跃岩,潘月,张秋香,崔树茂. 青少年正畸患者釉质脱矿的发生与口腔菌群及分泌型免疫球蛋白A的关系[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(5): 614-620. |
| [3] | 刘艺,郑博文,刘奕. 正畸诱导性牙根吸收防治策略的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(5): 662-669. |
| [4] | 赵美林,赵依琼,黄姣. Ⅲ期C级牙周炎正畸患者上前牙龈乳头缺陷伴牙龈退缩1例[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(3): 333-340. |
| [5] | 魏志,刘畅,王艳,赖文莉. 不同尺寸和材料的初始弓丝对正畸治疗中初始疼痛影响的系统评价与贝叶斯网状Meta分析[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(3): 366-379. |
| [6] | 杨惠宇,邓雅兰,任世睿,王诗萌,蔡和,程立,胡涛. 四川省65~74岁老年人口腔卫生服务利用状况及影响因素[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(3): 380-389. |
| [7] | 陆萌,陈文川,高一. 龈下牙体缺损修复中预防牙周疾病的策略[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2025, 52(2): 238-245. |
| [8] | 勾俊卓,朱亚芬,姜定卓,吴志芳. 替牙期正畸治疗对牙根发育影响的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(6): 662-668. |
| [9] | 潘珮玥,周婧,黄超,于乐,唐甜. 埋伏牙正畸治疗的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(6): 669-676. |
| [10] | 李榕,赵青. 基于颞下颌关节思考成人安氏Ⅱ2分类错 畸形的治疗[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(6): 687-698. |
| [11] | 刘曼,孟耀,牛茂. 正畸复发研究领域中4种有前景的生物药物的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(6): 699-705. |
| [12] | 李娇娇,刘钧. 外伤牙早期固定正畸治疗的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(4): 498-504. |
| [13] | 陈梓柠,王浩,李倩雯,赵宁睿,王雪东. 种植钉支抗在口腔正畸领域的应用情况综述[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(3): 310-318. |
| [14] | 李东娜, 翟浩嫣, 刘春艳. 牙周正畸联合治疗的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(3): 326-336. |
| [15] | 薛晴,齐慧川,胡敏. 机械应力下初级纤毛在骨和颞下颌关节软骨改建中力学感知作用的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2024, 51(2): 201-207. |
|