
国际口腔医学杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 137-143.doi: 10.7518/gjkq.2024020
Jie Huang1( ),Qiannan Deng1,Yao Meng1,Man Liu2(
),Qiannan Deng1,Yao Meng1,Man Liu2( )
)
摘要:
恒牙迟萌是指恒牙萌出时间显著晚于正常萌出期的现象,不仅可引起患儿错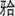 畸形,还可进一步影响患儿的咀嚼、发音功能与面容美观,严重时将损害患儿正常生长发育及心理健康,给家长带来负担。其发生以个别恒牙较常见,但部分患儿出现多颗恒牙迟萌。多颗恒牙迟萌病因复杂,除局部机械因素外,还可能与环境(如疾病、营养、感染、放射、药物)、遗传等因素具有相关性,本文就以上因素作一综述,以期为多颗恒牙迟萌的病因学研究及临床诊断提供思路。
畸形,还可进一步影响患儿的咀嚼、发音功能与面容美观,严重时将损害患儿正常生长发育及心理健康,给家长带来负担。其发生以个别恒牙较常见,但部分患儿出现多颗恒牙迟萌。多颗恒牙迟萌病因复杂,除局部机械因素外,还可能与环境(如疾病、营养、感染、放射、药物)、遗传等因素具有相关性,本文就以上因素作一综述,以期为多颗恒牙迟萌的病因学研究及临床诊断提供思路。
中图分类号:
| 1 | 葛立宏. 儿童口腔医学[M]. 5版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2020: 74. |
| Ge LH. Pediatric dentistry[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2020: 74. | |
| 2 | Esan TA, Mothupi KA, Schepartz LA. Permanent tooth emergence: timing and sequence in a sample of Black Southern African children[J]. Am J Phys Anthropol, 2018, 167(4): 827-839. |
| 3 | 张亚钦, 李辉, 武华红, 等. 中国九市四至七岁儿童乳恒牙替换及其与体格生长的相关性分析[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2020, 58(3): 206-212. |
| Zhang YQ, Li H, Wu HH, et al. Timing of permanent tooth emergence and its association with physical growth among children aged from four to seven years in nine cities of China[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2020, 58(3): 206-212. | |
| 4 | 曹艳艳, 张晓丹, 王晓斐, 等. 哈尔滨市10 248名儿童恒牙萌出情况的调查[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2018, 32(1): 41-44. |
| Cao YY, Zhang XD, Wang XF, et al. Eruption situation of permanent teeth in 10 248 children in Harbin[J]. J Mod Stomatol, 2018, 32(1): 41-44. | |
| 5 | Suri L, Gagari E, Vastardis H. Delayed tooth eruption: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. A lite-rature review[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2004, 126(4): 432-445. |
| 6 | Makino E, Tsujino K, Ishii T, et al. Difference in bilateral timing of eruption of permanent teeth[J]. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll, 2018, 59(4): 277-284. |
| 7 | Almonaitiene R, Balciuniene I, Tutkuviene J. Factors influencing permanent teeth eruption. Part one: general factors[J]. Stomatologija, 2010, 12(3): 67-72. |
| 8 | Rahul M, Ashima G, Akshat G. Arrested root growth and concomitant failure of eruption of a developing tooth following open reduction and internal fixation of a pediatric mandibular fracture[J]. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent, 2018, 36(2): 220-222. |
| 9 | Torlińska-Walkowiak N, Majewska KA, Kędzia A, et al. Clinical implications of growth hormone deficiency for oral health in children: a systematic review[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(16): 3733. |
| 10 | Partyka M, Chałas R, Dunin-Wilczyńska I, et al. Influence of growth hormone therapy on selected dental and skeletal system parameters[J]. Ann Agric Environ Med, 2018, 25(1): 60-65. |
| 11 | Kozma A, Teodorescu MI, Constantin AT, et al. Dento-maxillary changes in children with congenital hypothyroidism. Mini review and clinical cases[J]. Rom J Leg Med, 2019, 27(4): 382-387. |
| 12 | Kamarthi N, Venkatraman S, Patil PB. Dental fin-dings in the diagnosis of idiopathic hypoparathyroi-dism[J]. Ann Saudi Med, 2013, 33(4): 411-413. |
| 13 | 赵迪芳, 关淑元, 樊怡, 等. 特发性甲状旁腺功能减退症对大鼠牙萌出的影响[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2021, 56(9): 880-891. |
| Zhao DF, Guan SY, Fan Y, et al. Effects of idiopa-thic hypoparathyroidism on tooth eruption of rats[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2021, 56(9): 880-891. | |
| 14 | Tabakcilar D, Bundak R, Gencay K. Dental age in precocious and delayed puberty periods[J]. Eur J Dent, 2021, 15(3): 539-545. |
| 15 | Davidopoulou S, Chatzigianni A. Craniofacial morphology and dental maturity in children with reduced somatic growth of different aetiology and the effect of growth hormone treatment[J]. Prog Orthod, 2017, 18(1): 10. |
| 16 | Alvarez JO. Nutrition, tooth development, and dental caries[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 1995, 61(2): 410S-416S. |
| 17 | Uwitonze AM, Rahman S, Ojeh N, et al. Oral manifestations of magnesium and vitamin D inadequacy[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2020, 200: 105636. |
| 18 | Goltzman D. Functions of vitamin D in bone[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2018, 149(4): 305-312. |
| 19 | Xavier TA, Madalena IR, da Silva RAB, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is a risk factor for delayed tooth eruption associated with persistent primary tooth[J]. Acta Odontol Scand, 2021, 79(8): 600-605. |
| 20 | Brodetska L, Natrus L, Lisakovska O, et al. The re-gulatory role of the RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling pathway in the mechanisms of tooth eruption in patients with impacted teeth[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2020, 20(1): 261. |
| 21 | Crincoli V, Cazzolla AP, Di Comite M, et al. Evaluation of vitamin D (25OHD), bone alkaline phosphatase (BALP), serum calcium, serum phosphorus, ionized calcium in patients with mandibular third molar impaction. An observational study[J]. Nu-trients, 2021, 13(6): 1938. |
| 22 | Reddy P, Edwards LR. Magnesium supplementation in vitamin D deficiency[J]. Am J Ther, 2019, 26(1): e124-e132. |
| 23 | Rodríguez-Ortiz ME, Canalejo A, Herencia C, et al. Magnesium modulates parathyroid hormone secretion and upregulates parathyroid receptor expression at moderately low calcium concentration[J]. Ne-phrol Dial Transplant, 2014, 29(2): 282-289. |
| 24 | Malmgren B, Tsilingaridis G, Monsef-Johansson N, et al. Bisphosphonate therapy and tooth development in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2020, 107(2): 143-150. |
| 25 | Tuncer I, Delilbasi C, Deniz E, et al. Effects of pamidronate administration on tooth eruption and mandibular growth in new born rats[J]. J Istanb Univ Fac Dent, 2017, 51(1): 8-14. |
| 26 | Isawa M, Karakawa A, Sakai N, et al. Biological effects of anti-RANKL antibody and zoledronic acid on growth and tooth eruption in growing mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 19895. |
| 27 | Näsman M, Hammarström L. Influence of the antineoplastic agent cyclophosphamide on dental deve-lopment in rat molars[J]. Acta Odontol Scand, 1996, 54(5): 287-294. |
| 28 | Matsuo S, Toda-Nakamura M, Oka K, et al. Cyclophosphamide promotes arrested development of the dental root in mice[J]. J Hard Tissue Biol, 2020, 29(2): 63-70. |
| 29 | Li ZZ, Wang HT, Lee GY, et al. Bleomycin: a novel osteogenesis inhibitor of dental follicle cells via a TGF-β1/SMAD7/RUNX2 pathway[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2021, 178(2): 312-327. |
| 30 | Piekoszewska-Ziętek P, Olczak-Kowalczyk D, Pań‑ czyk-Tomaszewska M, et al. Developmental abnormalities of teeth in children with nephrotic syndrome[J]. Int Dent J, 2022, 72(4): 572-577. |
| 31 | Carrillo CM, Corrêa FN, Lopes NN, et al. Dental anomalies in children submitted to antineoplastic therapy[J]. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 2014, 69(6): 433-437. |
| 32 | Merzel JJ, Novaes PP, Furlan SS. The effects of local trauma to the enamel-related periodontal tissues in the eruption of the rat incisor[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2000, 45(4): 323-333. |
| 33 | de Araujo AM, Gomes CC, de Almeida SM, et al. Effect of radiotherapy on the eruption rate and morphology of the odontogenic region of rat incisors[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2014, 59(11): 1242-1248. |
| 34 | Coady JM, Santangelo MV, Toto PD. Gamma-irra-diated mouse incisor[J]. J Dent Res, 1967, 46(4): 681-685. |
| 35 | Hauk MJ, Moss ME, Weinberg GA, et al. Delayed tooth eruption: association with severity of HIV infection[J]. Pediatr Dent, 2001, 23(3): 260-262. |
| 36 | Psoter WJ, Nelson EM, Psoter KJ, et al. Delayed tooth emergence in children infected with human immunodeficiency virus[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2016, 122(4): 442-447. |
| 37 | Ramos-Gomez FJ, Petru A, Hilton JF, et al. Oral manifestations and dental status in paediatric HIV infection[J]. Int J Paediatr Dent, 2000, 10(1): 3-11. |
| 38 | Alencar PNB, Lima MCF, Carvalho IF, et al. Radiographic evaluation of dental anomalies in patients with congenital Zika virus syndrome[J]. Braz Oral Res, 2021, 35: e043. |
| 39 | Gomes PN, Azevedo ID, do Amaral BA, et al. Microcephaly as a risk factor for dental alterations: a case-control study[J]. Oral Dis, 2023, 29(5): 2265-2271. |
| 40 | Medina DT, Santos APPD, Rodrigues FMDF, et al. Oral manifestations of congenital Zika virus infection in children with microcephaly: 18-month follow-up case series[J]. Spec Care Dentist, 2022, 42(4): 343-351. |
| 41 | da Costa CCG, Dias VO, Martelli DRB, et al. First cases of oligodontia as a manifestation of the Zika virus congenital syndrome[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2022, 134(4): e261-e266. |
| 42 | Macho VMP, Coelho AS, Veloso E Silva DM, et al. Oral manifestations in pediatric patients with coe-liac disease-a review article[J]. Open Dent J, 2017, 11: 539-545. |
| 43 | Condò R, Costacurta M, Maturo P, et al. The dental age in the child with coeliac disease[J]. Eur J Pae-diatr Dent, 2011, 12(3): 184-188. |
| 44 | Paul SP, Kirkham EN, John R, et al. Coeliac disease in children-an update for general dental practitioners[J]. Br Dent J, 2016, 220(9): 481-485. |
| 45 | Mina S, Riga C, Azcurra AI, et al. Oral ecosystem alterations in celiac children: a follow-up study[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2012, 57(2): 154-160. |
| 46 | Geller F, Feenstra B, Zhang H, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies four loci associated with eruption of permanent teeth[J]. PLoS Genet, 2011, 7(9): e1002275. |
| 47 | Puranik RS, Puranik SR, Hallur N, et al. GAPO syndrome-a rare cause of osteomyelitis of jaws; report of 4 cases with a brief review of the literature[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 76(6): 1216-1225. |
| 48 | Silva-Andrade N, López-Ortega K, Gallottini M. Orofacial features and medical profile of eight individuals with Kabuki syndrome[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2019, 24(5): e630-e635. |
| 49 | Xin YJ, Liu Y, Li J, et al. A novel lncRNA mediates the delayed tooth eruption of cleidocranial dysplasia[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(17): 2729. |
| 50 | Cerezo-Cayuelas M, Pérez-Silva A, Serna-Muñoz C, et al. Orthodontic and dentofacial orthopedic treatments in patients with ectodermal dysplasia: a systematic review[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2022, 17(1): 376. |
| 51 | Esposito L, Poletti L, Maspero C, et al. Hyper-IgE syndrome: dental implications[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2012, 114(2): 147-153. |
| 52 | Taqi D, Moussa H, Schwinghamer T, et al. Missing and unerupted teeth in osteogenesis imperfecta[J]. Bone, 2021, 150: 116011. |
| 53 | Zhang YL, Ji DR, Li L, et al. ClC-7 regulates the pattern and early development of craniofacial bone and tooth[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(5): 1387-1400. |
| 54 | Yamaguchi T, Hosomichi K, Shirota T, et al. Primary failure of tooth eruption: etiology and management[J]. Jpn Dent Sci Rev, 2022, 58: 258-267. |
| 55 | Takahashi A, Nagata M, Gupta A, et al. Autocrine regulation of mesenchymal progenitor cell fates orchestrates tooth eruption[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(2): 575-580. |
| 56 | Assiry AA, Albalawi AM, Zafar MS, et al. KMT2C, a histone methyltransferase, is mutated in a family segregating non-syndromic primary failure of tooth eruption[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 16469. |
| 57 | 代佳琪, 游梦, 郭文豪, 等. 区域性牙发育不良三例[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2020, 55(7): 501-503. |
| Dai JQ, You M, Guo WH, et al. Regional odontodysplasia: a report of three cases[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2020, 55(7): 501-503. | |
| 58 | Nijakowski K, Woś P, Surdacka A. Regional odontodysplasia: a systematic review of case reports[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(3): 1683. |
| 59 | Alotaibi O, Alotaibi G, Alfawaz N. Regional odontodysplasia: an analysis of 161 cases from 1953 to 2017[J]. Saudi Dent J, 2019, 31(3): 306-310. |
| 60 | Frazier-Bowers SA, Koehler KE, Ackerman JL, et al. Primary failure of eruption: further characterization of a rare eruption disorder[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2007, 131(5): 578.e1-578.e11. |
| 61 | Sivakumar A, Valiathan A, Gandhi S, et al. Idiopa-thic failure of eruption of multiple permanent teeth: report of 2 adults with a highlight on molecular biology[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2007, 132(5): 687-692. |
| [1] | 杨静,柳登高. 内镜下激光碎石术治疗唾液腺结石病的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2023, 50(6): 704-710. |
| [2] | 刘晓琳,任群,高晓哲,白九平,王宇,李向军. 458例上切牙区多生牙的临床资料分析[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2023, 50(1): 61-65. |
| [3] | 曾杨林,谭学莲,宋东哲,黄定明. 牙根内吸收临床诊治方法的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2022, 49(5): 561-568. |
| [4] | 查蕴宸,张佳佳,孔卫东. 原发性牙齿萌出障碍病因的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2022, 49(4): 386-391. |
| [5] | 董栩,徐欣. 牙隐裂临床研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2021, 48(6): 668-674. |
| [6] | 陶慧骞,但红霞. 口腔黏膜瘙痒症的病因与治疗[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2021, 48(1): 119-124. |
| [7] | 赵文俊,郝晓琪,王凯利,刘媛媛,唐蓓,任家银,郑广宁. 对吻磨牙的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2021, 48(1): 96-101. |
| [8] | 吴勇志,尧可,陈思宇,黄能文,王了. 多生牙及其诊断治疗[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2020, 47(3): 311-317. |
| [9] | 田国莉,江潞,陈谦明,曾昕. 味觉异常的病因和治疗研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2020, 47(3): 356-361. |
| [10] | 吕靖,彭静,栗璞. 双生子颅面深度和上气道宽度的遗传和环境因素研究[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2020, 47(2): 175-181. |
| [11] | 刘小旭,马坚,石冰,黄永清. Pai综合征的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2019, 46(3): 339-342. |
| [12] | 张清彬, 谭乐成. 磨牙症的病因研究与治疗进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2018, 45(5): 497-500. |
| [13] | 蔡东霖, 卢锐. 儿童复发性阿弗他溃疡病因学的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2018, 45(2): 145-149. |
| [14] | 张清彬. 张清彬谈张口受限[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2017, 44(5): 495-502. |
| [15] | 谢成佳, 葛少华. 牙骨质撕裂的诊治进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2017, 44(3): 315-319. |
|